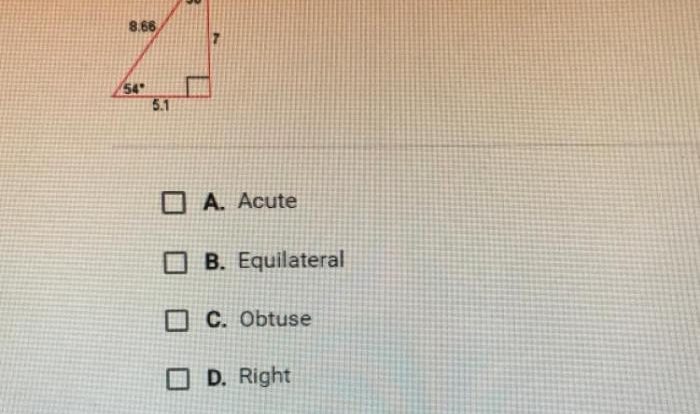
As given KLMN is a trapezoid takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with gaya bahasa santai tapi bahasa baku into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Trapezoids, with their intriguing combination of parallel bases and non-parallel sides, are geometric shapes that offer a wealth of mathematical properties and practical applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of trapezoids, exploring their characteristics, properties, geometric relationships, and real-world uses.
Definition of a Trapezoid: Given Klmn Is A Trapezoid
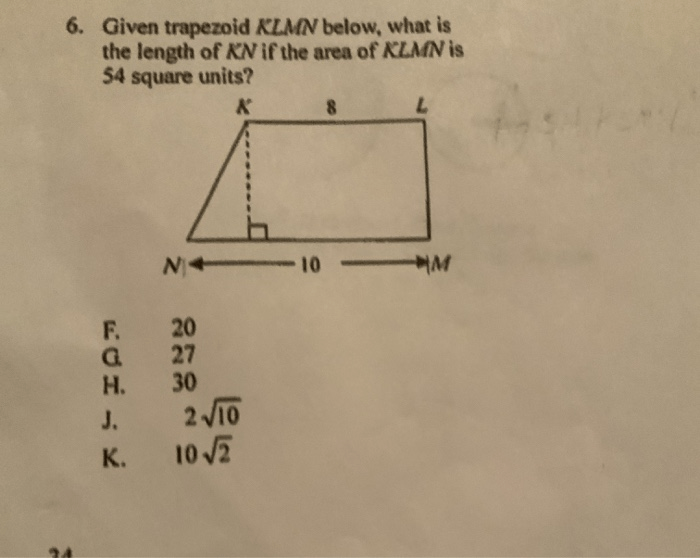
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides. The parallel sides are called bases, and the non-parallel sides are called legs.
Trapezoids are classified into two types: isosceles and scalene. An isosceles trapezoid has two congruent legs, while a scalene trapezoid has two non-congruent legs.
Types of Trapezoids
Isosceles Trapezoid
An isosceles trapezoid has two congruent legs. This means that the two non-parallel sides of the trapezoid are equal in length.
Scalene Trapezoid
A scalene trapezoid has two non-congruent legs. This means that the two non-parallel sides of the trapezoid are not equal in length.
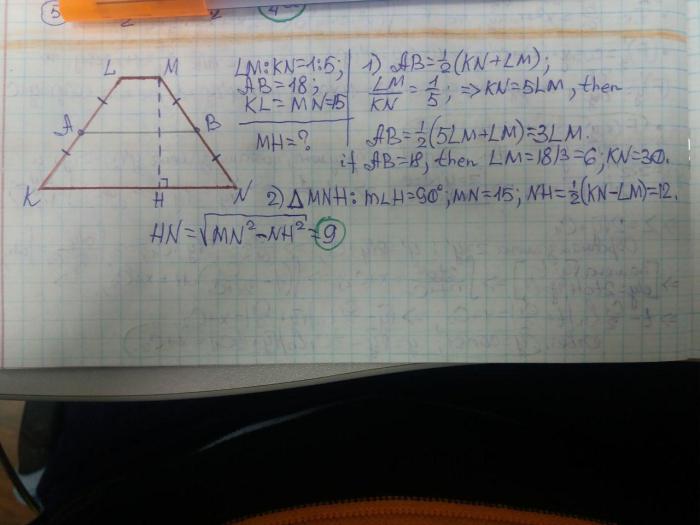
Given KLMN is a trapezoid, with KL being the shorter base. If you’re interested in exploring the depths of a different kind of trapezoid, check out this sinks of gandy cave map . Back to our trapezoid KLMN, the diagonals KM and LN intersect at point O.
Properties of Trapezoid KLMN
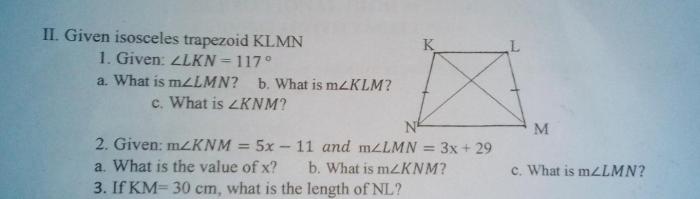
Trapezoid KLMN is a quadrilateral with two parallel sides. The parallel sides are called bases, and the non-parallel sides are called legs. In this case, KL and MN are the bases, and KM and LN are the legs.The properties of trapezoid KLMN include:
- The sum of the interior angles on the same side of a transversal is 180 degrees.
- The diagonals of a trapezoid bisect each other.
- The area of a trapezoid is equal to the product of the height and the average of the bases.
- The perimeter of a trapezoid is equal to the sum of the lengths of the four sides.
Length of the Bases and Non-Parallel Sides
The length of the bases of trapezoid KLMN are KL = 10 cm and MN = 15 cm. The length of the non-parallel sides are KM = 8 cm and LN = 12 cm.
Area and Perimeter of Trapezoid KLMN
The height of trapezoid KLMN is 6 cm. The area of trapezoid KLMN is:“`Area = (1/2)
- (KL + MN)
- h
Area = (1/2)
- (10 cm + 15 cm)
- 6 cm
Area = 75 square cm“`The perimeter of trapezoid KLMN is:“`Perimeter = KL + MN + KM + LNPerimeter = 10 cm + 15 cm + 8 cm + 12 cmPerimeter = 45 cm“`
Diagonals of Trapezoid KLMN, Given klmn is a trapezoid
The diagonals of trapezoid KLMN are KM and LN. The diagonals of a trapezoid bisect each other, which means that they divide each other into two equal parts.The diagonals of trapezoid KLMN also form two triangles, KLM and LMN. These triangles are congruent, which means that they have the same shape and size.
Geometric Relationships within Trapezoid KLMN
Trapezoid KLMN exhibits several interesting geometric relationships between its sides and segments. Understanding these relationships is crucial for comprehending the properties and characteristics of this quadrilateral.
Relationship between Bases and Non-Parallel Sides
In trapezoid KLMN, the bases are the parallel sides, denoted by KL and MN. The non-parallel sides are denoted by KM and LN. These sides have specific relationships with each other:
- The non-parallel sides are congruent:KM = LN.
- The bases are not necessarily congruent:KL ≠ MN.
Properties of the Midsegment of Trapezoid KLMN
The midsegment of a trapezoid is a line segment that connects the midpoints of the non-parallel sides. In trapezoid KLMN, the midsegment is denoted by PQ. This segment possesses the following properties:
- Parallel to the bases:PQ is parallel to both KL and MN.
- Half the sum of the bases:PQ = (KL + MN) / 2.
Inscribed and Circumscribed Circles of Trapezoid KLMN
An inscribed circle is a circle that lies inside a polygon and is tangent to all of its sides. A circumscribed circle is a circle that lies outside a polygon and passes through all of its vertices. In trapezoid KLMN, the inscribed circle is tangent to all four sides, while the circumscribed circle passes through all four vertices:
- Inscribed circle:The center of the inscribed circle lies at the intersection of the perpendicular bisectors of the non-parallel sides.
- Circumscribed circle:The center of the circumscribed circle lies at the intersection of the perpendicular bisectors of the diagonals.
Understanding these geometric relationships within trapezoid KLMN provides valuable insights into the properties and characteristics of this shape.
Applications of Trapezoids in Real-World Contexts
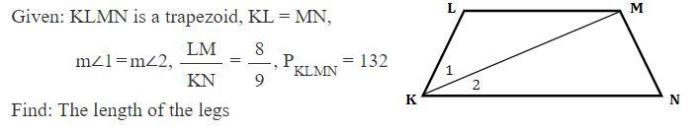
Trapezoids, with their unique shape and versatile properties, find numerous applications in the real world. From architectural designs to mathematical calculations, trapezoids play a crucial role in various fields.
Real-World Objects Shaped Like Trapezoids
Many everyday objects incorporate trapezoidal shapes. For instance, the sails of sailboats utilize trapezoids to capture wind effectively. Similarly, the shape of a kite is often trapezoidal, providing stability and lift during flight.
Structural Advantages of Trapezoids in Architecture and Engineering
Trapezoids offer several structural advantages in architecture and engineering. Their shape provides inherent stability and strength. For example, trapezoidal roof trusses are commonly used in buildings to distribute weight evenly and withstand external forces.
Applications of Trapezoids in Mathematics and Physics
In mathematics and physics, trapezoids are used to solve various problems. The trapezoidal rule, a numerical integration technique, approximates the area under a curve using trapezoids. Additionally, trapezoids are employed in calculating the moment of inertia of complex shapes.
Questions Often Asked
What is the definition of a trapezoid?
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides, known as the bases, and two non-parallel sides, known as the legs.
How do you calculate the area of a trapezoid?
The area of a trapezoid is given by the formula: Area = (1/2) – (sum of the bases) – (height), where height is the perpendicular distance between the bases.
What are the different types of trapezoids?
There are several types of trapezoids, including isosceles trapezoids (where the non-parallel sides are equal in length), scalene trapezoids (where the non-parallel sides are not equal in length), and right trapezoids (where one of the non-parallel sides is perpendicular to the bases).