Microscope fill in the blank answers are an essential tool for students and professionals in various fields who need to understand the principles and applications of microscopy. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of different types of microscopes, their components, techniques, applications, and care and maintenance.
Microscopy has revolutionized our understanding of the world around us, allowing us to explore the intricate details of cells, tissues, and materials. From basic compound microscopes to advanced electron microscopes, these instruments have played a pivotal role in scientific research, medical diagnostics, and industrial quality control.
Types of Microscopes
Microscopy is a vital technique used in various scientific fields, including biology, chemistry, and medicine. It enables scientists to observe and study objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. Over the years, different types of microscopes have been developed, each with its own unique features and applications.
Types of Microscopes
The primary types of microscopes are:
- Light Microscope
- Electron Microscope
- Scanning Probe Microscope
Each type of microscope has its own advantages and disadvantages, making it suitable for different applications. The table below provides a summary of the features, applications, and advantages of each type:
| Type of Microscope | Features | Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Microscope | Uses visible light to illuminate the specimen | Biological sciences, medicine | Relatively inexpensive, easy to use |
| Electron Microscope | Uses a beam of electrons to illuminate the specimen | Materials science, nanotechnology | High resolution, can magnify objects up to 1 million times |
| Scanning Probe Microscope | Uses a sharp probe to scan the surface of the specimen | Surface science, nanotechnology | Can create three-dimensional images of surfaces |
Components of a Microscope
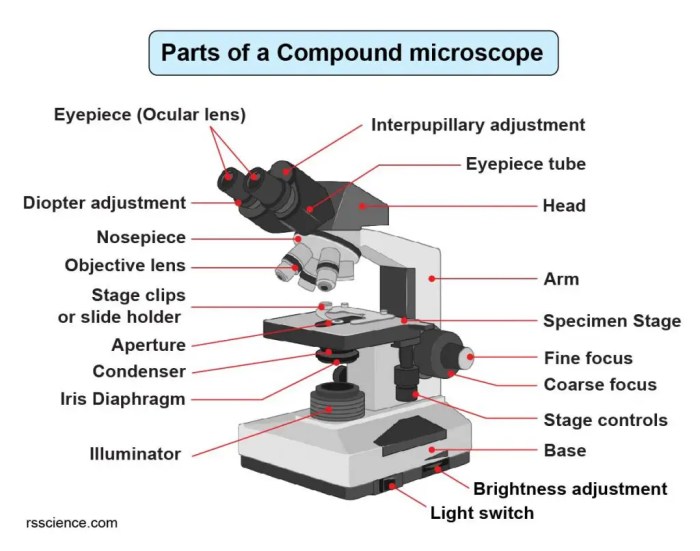
A microscope is a scientific instrument that allows us to observe and study tiny objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye. Microscopes are used in a wide variety of fields, including biology, chemistry, and medicine.The key components of a microscope include the eyepiece, objective lenses, stage, and illumination system.The
eyepiece is the lens that the user looks through. It magnifies the image of the object being viewed.The objective lenses are the lenses that are located at the bottom of the microscope. They magnify the image of the object being viewed.The
stage is the platform on which the object being viewed is placed.The illumination system provides light to the object being viewed.The following diagram illustrates the arrangement and function of these components:[Diagram of a microscope]
Microscope Techniques
Microscope techniques encompass various methods used to prepare and examine specimens under a microscope. These techniques play a crucial role in advancing scientific research and understanding the intricate details of biological and non-biological materials.
Principles of Light Microscopy and Electron Microscopy
Light microscopyutilizes visible light to illuminate specimens, allowing for the observation of structures and features ranging in size from micrometers to millimeters. The resolving power of light microscopes is limited by the wavelength of visible light, typically around 200 nanometers, which restricts the level of detail that can be visualized.
Electron microscopy, on the other hand, employs a beam of electrons to interact with specimens. This technique offers much higher resolving power than light microscopy, allowing for the visualization of structures at the atomic level. However, electron microscopy requires specialized sample preparation and can only be performed in a vacuum environment.
Specimen Preparation and Examination
Preparing specimens for microscopy involves a series of steps to enhance their visibility and preserve their structural integrity. These steps typically include:
- Fixation: Preserving the specimen’s structure by treating it with chemicals.
- Embedding: Encasing the specimen in a supporting material for sectioning.
- Sectioning: Creating thin slices of the specimen for examination.
- Staining: Enhancing the contrast of specific structures within the specimen.
Once prepared, the specimen is placed on a microscope slide and examined under the appropriate magnification and illumination conditions. The microscopist can adjust the focus, aperture, and other settings to optimize the image quality and visualize the desired features.
Staining Techniques in Microscopy
Staining techniques play a vital role in microscopy by enhancing the contrast and visibility of specific structures within a specimen. Different staining methods are employed to target specific components or properties of the specimen, such as:
| Staining Technique | Target |
|---|---|
| Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) | Nucleus and cytoplasm |
| Gram staining | Bacterial cell wall composition |
| Immunohistochemistry | Specific proteins or antigens |
| Fluorescence microscopy | Molecules or structures that emit light when excited |
Applications of Microscopy

Microscopy has revolutionized our understanding of the world at the microscopic level. Its applications span diverse fields, driving scientific research and technological advancements.
In biology, microscopes have enabled the study of cells, tissues, and microorganisms. They have aided in understanding cellular processes, disease mechanisms, and the development of new medical treatments.
Medicine
- Diagnosing diseases by examining tissue samples
- Studying the behavior of bacteria and viruses
- Developing new drugs and therapies
In materials science, microscopes have allowed scientists to analyze the structure and properties of materials. This has led to the development of stronger, lighter, and more durable materials for various applications.
Forensics, Microscope fill in the blank answers
- Examining evidence such as hair, fibers, and fingerprints
- Identifying trace amounts of substances
- Analyzing gunshot residue
In addition, microscopy has found applications in fields such as geology, archaeology, and environmental science. It has provided insights into the formation of rocks, the evolution of life, and the impact of human activities on the environment.
Care and Maintenance of Microscopes
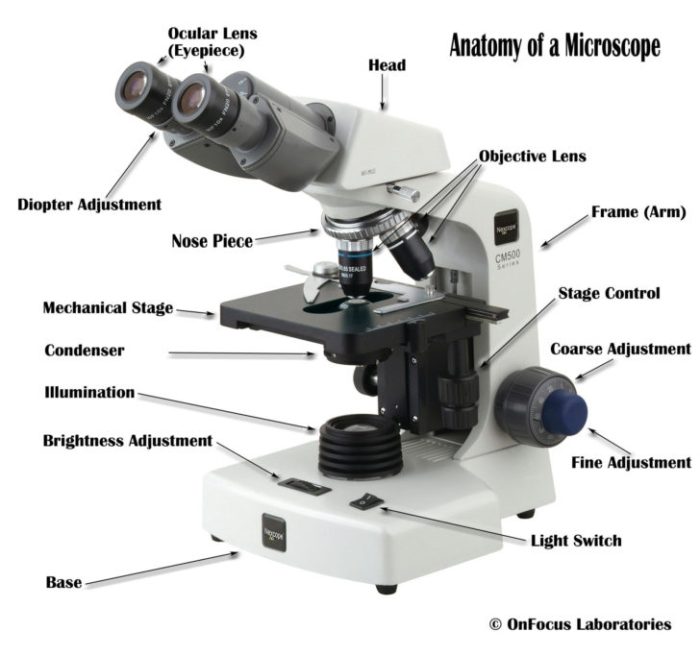

To ensure optimal performance and longevity of microscopes, proper handling, storage, and maintenance are essential. This includes regular cleaning and calibration to maintain accuracy and prevent damage.
Guidelines for Proper Handling and Storage
- Handle microscopes with care, avoiding sudden movements or dropping.
- Keep microscopes in a clean, dry environment, protected from dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
- Cover microscopes when not in use to prevent dust accumulation.
- Store microscopes upright to prevent damage to the objective lenses.
Regular Cleaning and Calibration
Regular cleaning and calibration are crucial for maintaining microscope performance and accuracy.
- Clean the microscope body, stage, and lenses regularly with a soft, lint-free cloth.
- Calibrate the microscope regularly to ensure accurate measurements and image quality.
- For more thorough cleaning, consult the manufacturer’s instructions or seek professional assistance.
FAQ Explained: Microscope Fill In The Blank Answers
What are the main types of microscopes?
There are three main types of microscopes: light microscopes, electron microscopes, and scanning probe microscopes.
What are the key components of a microscope?
The key components of a microscope include the eyepiece, objective lenses, stage, condenser, and illumination system.
What are the different staining techniques used in microscopy?
Common staining techniques used in microscopy include bright-field staining, dark-field staining, phase-contrast staining, and fluorescence staining.
What are the applications of microscopy?
Microscopy has a wide range of applications in fields such as biology, medicine, materials science, and forensics.
How do I care for and maintain my microscope?
Proper care and maintenance of your microscope is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for cleaning, storage, and calibration.