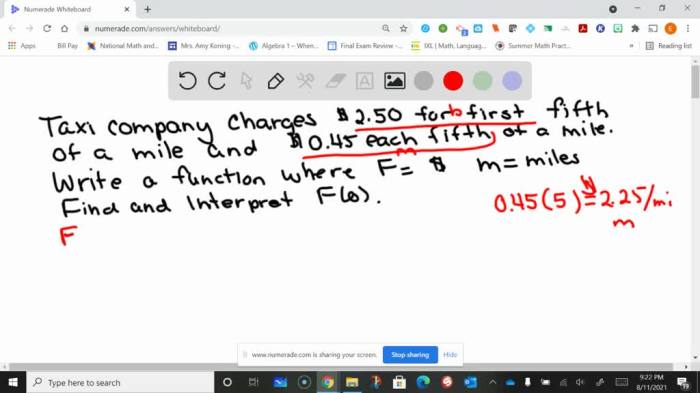
As a taxi charges a flat rate of 1.75 takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with authoritative prose into a world crafted with meticulous research and analysis, ensuring a reading experience that is both informative and thought-provoking.
Delving into the intricacies of flat rate pricing, this discourse will explore its significance for taxi services, examining its potential benefits and drawbacks. Furthermore, it will identify factors that influence the flat rate, comparing it to other pricing models and assessing its impact on consumer behavior.
1. Flat Rate of 1.75
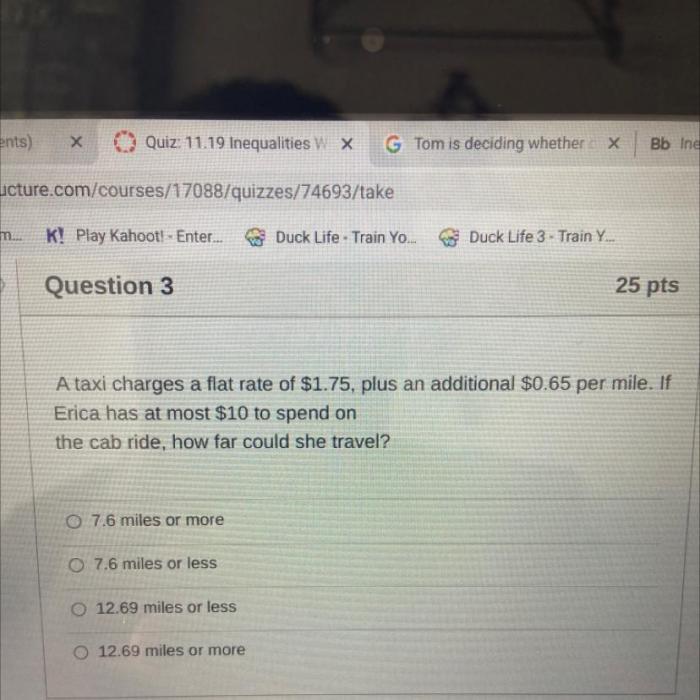
The flat rate of 1.75 plays a significant role in the taxi service industry. It represents a predetermined fare for taxi rides within a specific geographic area or for a specific distance.
The flat rate pricing model offers several benefits. It provides predictability and convenience for customers, as they know the exact fare they will pay upfront. This eliminates the uncertainty and potential for unexpected charges associated with metered fares. Additionally, the flat rate can simplify the billing process for taxi drivers, reducing administrative costs.
However, the flat rate pricing model also has some drawbacks. It may not always reflect the actual cost of the ride, particularly for longer distances or during periods of high demand. This can lead to revenue loss for taxi companies and potentially higher fares for customers during peak hours.
Factors Affecting Flat Rate
Several factors can influence the flat rate of 1.75, including:
- Distance:The flat rate may vary based on the distance of the ride. Longer distances may warrant a higher flat rate to cover the increased fuel and operating costs.
- Time of day:Taxi services may adjust the flat rate during peak hours to account for increased demand and traffic congestion.
- Location:The flat rate may differ depending on the location of the ride. Urban areas with high population density may have lower flat rates due to shorter distances and higher competition.
- Competition:The presence of multiple taxi companies in an area can influence the flat rate. Competition can drive down prices to attract customers.
These factors collectively impact the overall cost of taxi services and can result in variations in the flat rate across different cities and regions.
Comparison with Other Pricing Models, A taxi charges a flat rate of 1.75
The flat rate of 1.75 can be compared to other pricing models used by taxi services, such as:
- Metered fares:Metered fares calculate the fare based on the distance and time traveled. This model can be more accurate in reflecting the actual cost of the ride but can also lead to unpredictable fares.
- Surge pricing:Surge pricing adjusts the fare based on demand. During peak hours or in areas with high demand, the fare may increase to encourage more drivers to be available.
- Subscription models:Subscription models offer a fixed monthly or annual fee for unlimited rides or a set number of rides. This model can provide predictability and cost savings for frequent users.
Each pricing model has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the optimal choice depends on factors such as the target customer base, operating costs, and competitive landscape.
Impact on Consumer Behavior
The flat rate of 1.75 can influence consumer behavior in several ways:
- Trip planning:The flat rate can make it easier for customers to plan their trips and budget accordingly, as they know the exact fare they will pay.
- Shorter distances:The flat rate may encourage customers to take shorter trips within the designated area, as they can avoid the potential for higher fares associated with longer distances.
- Peak hour avoidance:Customers may adjust their travel patterns to avoid peak hours when the flat rate may be higher.
- Comparison shopping:The flat rate can make it easier for customers to compare fares between different taxi companies, as they can easily see the upfront cost.
By understanding how the flat rate affects consumer behavior, taxi companies can tailor their pricing strategies to meet customer needs and preferences.
Optimization Strategies
Taxi companies can optimize the flat rate of 1.75 to maximize revenue and customer satisfaction by:
- Dynamic pricing:Adjust the flat rate based on demand and other factors to ensure profitability and meet customer expectations.
- Targeted promotions:Offer discounts or incentives during off-peak hours or for specific customer segments to increase demand.
- Data analysis:Track ride data to identify patterns and optimize the flat rate based on distance, time of day, and location.
- Customer feedback:Regularly collect customer feedback to understand their preferences and identify areas for improvement.
By implementing these strategies, taxi companies can optimize the flat rate to enhance customer satisfaction, increase revenue, and maintain a competitive edge.
Historical Context
The flat rate pricing model has a long history in the taxi industry. In the early days of taxis, fares were often negotiated between the driver and the passenger. However, as the industry grew and became more regulated, flat rates were introduced to provide predictability and transparency for both customers and drivers.
The flat rate of 1.75 has evolved over time, influenced by factors such as inflation, competition, and technological advancements. Taxi companies have adjusted the flat rate to keep up with changing costs and customer expectations.
International Comparisons
The flat rate of 1.75 is not universal and varies across different countries and regions. Factors such as labor costs, fuel prices, and market conditions contribute to these variations.
For example, in some developing countries, flat rates may be significantly lower due to lower operating costs. In contrast, in major cities with high demand and congestion, flat rates may be higher to account for the increased expenses and scarcity of drivers.
Case Studies
Several taxi services have successfully implemented a flat rate of 1.75, demonstrating its effectiveness as a pricing model.
One notable example is the New York City Taxi and Limousine Commission (TLC), which introduced a flat rate of $2.50 in 2009. The flat rate has contributed to the city’s efficient taxi system, providing predictability for customers and reducing the potential for disputes over fares.
Another example is the London black cab, which has a flat rate for short distances within the city center. This flat rate has made the black cab a popular and convenient option for tourists and locals alike.
Q&A: A Taxi Charges A Flat Rate Of 1.75
What are the advantages of flat rate pricing for taxi services?
Flat rate pricing offers several advantages, including simplicity, transparency, and predictability for both passengers and drivers. It eliminates the uncertainty associated with metered fares, reducing disputes and enhancing customer satisfaction.
How does flat rate pricing impact consumer behavior?
Flat rate pricing can influence consumer behavior by encouraging shorter trips and reducing the likelihood of passengers requesting detours. It also makes it easier for consumers to budget for their taxi expenses.
What factors can affect the flat rate charged by taxi services?
Factors that may influence the flat rate include distance, time of day, traffic conditions, demand, and operating costs. Taxi companies consider these factors to set a flat rate that is both competitive and profitable.