Match the human activities with their effects: this topic delves into the profound impact of human endeavors on the environment. From agriculture to urbanization, industrialization to tourism, this exploration unravels the intricate connections between human actions and their far-reaching consequences.
Agriculture, a cornerstone of civilization, has left an indelible mark on soil quality, water resources, and biodiversity. Industrialization, while driving economic growth, has also brought environmental degradation, social disparities, and health concerns. Urbanization, the concentration of populations in cities, has led to air and water pollution, along with significant social and economic shifts.
Agriculture and its effects
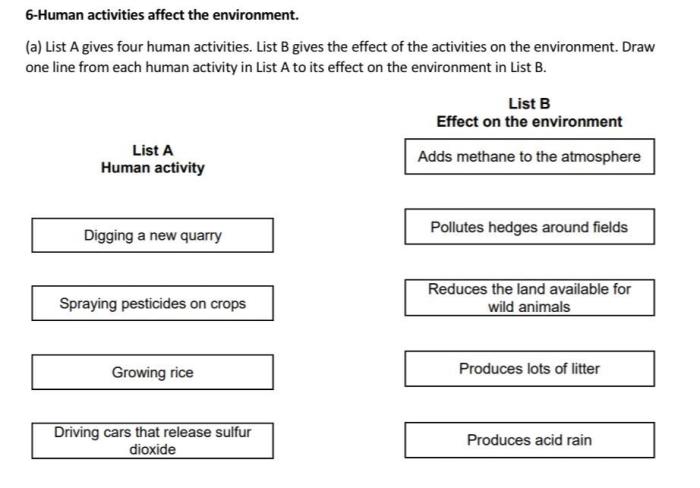
Agriculture has been a cornerstone of human civilization for millennia, providing sustenance and supporting societies. However, its practices have also had profound impacts on the environment.
Soil quality
- Agriculture can lead to soil degradation through erosion, compaction, and nutrient depletion.
- Erosion occurs when topsoil is removed by wind or water, reducing soil fertility and productivity.
- Compaction occurs when heavy machinery or livestock compress soil, reducing its ability to absorb water and nutrients.
- Nutrient depletion occurs when crops remove nutrients from the soil, which can lead to soil infertility if not replenished.
Water resources, Match the human activities with their effects
- Agriculture is a major consumer of water, particularly in irrigated regions.
- Irrigation can lead to water scarcity, salinization, and water pollution.
- Water scarcity occurs when demand for water exceeds supply, leading to competition and conflicts.
- Salinization occurs when salts accumulate in soil and water, reducing their productivity.
- Water pollution occurs when agricultural runoff, containing fertilizers and pesticides, enters water bodies.
Biodiversity
- Agriculture can lead to habitat loss and fragmentation, which can threaten biodiversity.
- Habitat loss occurs when natural areas are converted to agricultural land.
- Fragmentation occurs when natural habitats are divided into smaller and more isolated patches.
- Both habitat loss and fragmentation can reduce the abundance and diversity of species.
Industrialization and its consequences

Industrialization has brought about technological advancements and economic growth, but it has also had significant environmental and social consequences.
Environmental effects
- Industrialization has led to increased air and water pollution, as well as greenhouse gas emissions.
- Air pollution occurs when pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, are released into the atmosphere.
- Water pollution occurs when pollutants, such as heavy metals and chemicals, are released into water bodies.
- Greenhouse gas emissions contribute to climate change, leading to rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and other environmental impacts.
Social and economic consequences
- Industrialization has led to urbanization, which can strain infrastructure and social services.
- Urbanization occurs when people move from rural areas to cities in search of work and better opportunities.
- It can lead to overcrowding, housing shortages, and increased crime rates.
- Industrialization has also led to labor exploitation and income inequality.
- Labor exploitation occurs when workers are forced to work in unsafe or unhealthy conditions for low wages.
- Income inequality occurs when there is a large gap between the rich and the poor.
Impact on human health
- Industrialization has led to increased exposure to hazardous chemicals and pollutants.
- This can lead to respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
- Industrialization has also led to increased stress and mental health issues.
Urbanization and its influences
Urbanization is the process of people moving from rural areas to cities. It has had a profound impact on the environment, society, and economy.
Effects on air quality
- Urbanization can lead to increased air pollution due to increased traffic, industrial activity, and energy consumption.
- Air pollution can cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
Impact on water resources
- Urbanization can lead to increased water consumption and pollution.
- Water consumption can strain water supplies, especially in arid regions.
- Water pollution can occur from sewage, industrial runoff, and stormwater runoff.
Social and economic consequences
- Urbanization can lead to increased crime rates, poverty, and social inequality.
- Crime rates can increase due to overcrowding and lack of opportunities.
- Poverty can increase due to the high cost of living in urban areas.
- Social inequality can occur due to the unequal distribution of resources and opportunities.
Energy production and its implications: Match The Human Activities With Their Effects
Energy production is essential for modern society, but it also has significant environmental and social implications.
Environmental effects
- Energy production can lead to air and water pollution, as well as greenhouse gas emissions.
- Air pollution can occur from the burning of fossil fuels, which releases pollutants such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
- Water pollution can occur from the extraction and processing of fossil fuels, as well as from the disposal of nuclear waste.
- Greenhouse gas emissions contribute to climate change, leading to rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and other environmental impacts.
Social and economic implications
- Energy production can lead to conflicts over resources and land use.
- Conflicts can occur between different countries or regions over access to oil, gas, and other energy resources.
- Land use conflicts can occur between energy companies and other stakeholders, such as farmers and conservationists.
Impact on human health
- Energy production can lead to increased exposure to hazardous chemicals and pollutants.
- This can lead to respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
Transportation and its effects
Transportation is essential for moving people and goods, but it also has significant environmental and social impacts.
Impact on air quality
- Transportation is a major contributor to air pollution, particularly in urban areas.
- Air pollution from transportation can cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
Effects on land use
- Transportation infrastructure, such as roads and airports, can fragment natural habitats and displace wildlife.
- Habitat fragmentation can reduce the abundance and diversity of species.
- Displacement of wildlife can disrupt food chains and ecosystems.
Social and economic consequences
- Transportation can lead to increased traffic congestion, which can waste time and fuel.
- Traffic congestion can also lead to increased stress and anxiety.
- Transportation can also be expensive, especially in urban areas.
Tourism and its consequences
Tourism is a major industry that can bring economic benefits to communities, but it also has environmental and social consequences.
Environmental effects
- Tourism can lead to increased air and water pollution, as well as noise pollution.
- Air pollution can occur from increased traffic and energy consumption.
- Water pollution can occur from sewage and waste disposal.
- Noise pollution can occur from loudspeakers, vehicles, and other tourist activities.
Social and economic consequences
- Tourism can lead to increased crime rates and social inequality.
- Crime rates can increase due to the presence of large numbers of tourists and the associated increase in wealth.
- Social inequality can occur due to the unequal distribution of benefits from tourism.
Impact on cultural heritage
- Tourism can lead to the degradation of cultural heritage sites.
- This can occur due to increased foot traffic, pollution, and vandalism.
- The degradation of cultural heritage sites can damage the identity and sense of place for local communities.
Helpful Answers
What are the major environmental effects of agriculture?
Agriculture can lead to soil erosion, water pollution, and loss of biodiversity.
How does industrialization impact human health?
Industrialization can contribute to air pollution, which can cause respiratory problems and other health issues.
What are the social consequences of urbanization?
Urbanization can lead to increased crime, poverty, and social inequality.