ATI reproduction complications of pregnancy encompass a range of conditions that can arise during gestation and childbirth, potentially posing significant risks to both the mother and the developing fetus. Understanding these complications is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals alike, as early detection and management can significantly improve outcomes.
This comprehensive overview delves into the pathophysiology, symptoms, risk factors, and management strategies associated with various ATI reproduction complications of pregnancy, providing valuable insights for informed decision-making and optimal patient care.
Amniotic Fluid Embolism
Amniotic fluid embolism (AFE) is a rare but life-threatening obstetric emergency that occurs when amniotic fluid and fetal material enter the maternal circulation. The exact pathophysiology of AFE is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve a combination of mechanical obstruction, anaphylaxis, and inflammation.
Symptoms and Signs
- Sudden onset of respiratory distress
- Hypotension
- Coagulopathy
- Pulmonary edema
- Neurological symptoms (e.g., seizures, coma)
Risk Factors
- Advanced maternal age
- Multiple pregnancy
- Placental abruption
- Cesarean delivery
- Uterine rupture
Management, Ati reproduction complications of pregnancy
Management of AFE is supportive and includes:
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- Vasopressors
- Blood transfusions
- Mechanical ventilation
- Anticonvulsants
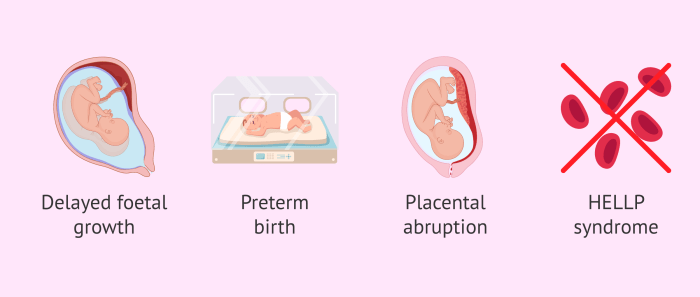
Placental Abruption
Placental abruption is the premature separation of the placenta from the uterine wall. It is a serious obstetric complication that can lead to fetal death, preterm birth, and maternal hemorrhage.
Pathophysiology
Placental abruption occurs when there is a disruption in the normal attachment of the placenta to the uterus. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Trauma (e.g., abdominal injury, motor vehicle accident)
- Preeclampsia
- Chronic hypertension
- Smoking
- Substance abuse
Symptoms and Signs
- Vaginal bleeding
- Abdominal pain
- Uterine tenderness
- Fetal distress
Risk Factors
- Advanced maternal age
- Previous placental abruption
- Multiple pregnancy
- Smoking
- Substance abuse
Management, Ati reproduction complications of pregnancy
Management of placental abruption depends on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, expectant management may be possible. In more severe cases, immediate delivery is necessary.
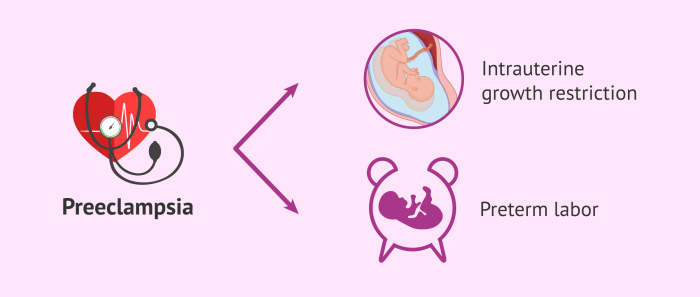
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a pregnancy-specific disorder characterized by hypertension and proteinuria. It is a major cause of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality.
Pathophysiology
The exact cause of preeclampsia is unknown, but it is thought to involve a combination of placental dysfunction, endothelial dysfunction, and inflammation.
Symptoms and Signs
- Hypertension
- Proteinuria
- Edema
- Headaches
- Visual disturbances
- Abdominal pain
Risk Factors
- First pregnancy
- Advanced maternal age
- Obesity
- Chronic hypertension
- Diabetes
- Family history of preeclampsia
Management, Ati reproduction complications of pregnancy
Management of preeclampsia involves close monitoring of maternal and fetal well-being. In mild cases, expectant management may be possible. In more severe cases, delivery may be necessary to prevent complications such as eclampsia and HELLP syndrome.
Eclampsia: Ati Reproduction Complications Of Pregnancy
Eclampsia is a severe form of preeclampsia that is characterized by seizures. It is a life-threatening condition for both the mother and the fetus.
Pathophysiology
The exact cause of eclampsia is unknown, but it is thought to be related to the same underlying mechanisms that cause preeclampsia.
Symptoms and Signs
- Seizures
- Hypertension
- Proteinuria
- Edema
- Headaches
- Visual disturbances
- Abdominal pain
Risk Factors
The same risk factors that are associated with preeclampsia are also associated with eclampsia.
Management, Ati reproduction complications of pregnancy
Management of eclampsia involves immediate delivery of the baby. Anticonvulsants are also used to control seizures.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is a common complication that can affect both the mother and the fetus.
Pathophysiology
Gestational diabetes is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demand of pregnancy. This can lead to high blood sugar levels.
Symptoms and Signs
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
Risk Factors
- Obesity
- Family history of diabetes
- Advanced maternal age
- Previous history of gestational diabetes
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
Management, Ati reproduction complications of pregnancy
Management of gestational diabetes involves diet, exercise, and medication to control blood sugar levels. In some cases, insulin therapy may be necessary.
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) is a condition in which the mother’s antibodies attack the baby’s red blood cells. This can lead to anemia, jaundice, and other complications.
Pathophysiology
HDN occurs when the mother and baby have different blood types. The most common cause of HDN is Rh incompatibility. In Rh incompatibility, the mother is Rh-negative and the baby is Rh-positive.
Symptoms and Signs
- Anemia
- Jaundice
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Hydrops fetalis
Risk Factors
- Rh incompatibility
- ABO incompatibility
- Previous history of HDN
- Multiple pregnancy
Management, Ati reproduction complications of pregnancy
Management of HDN involves preventing the development of antibodies in the mother. This can be done by administering Rh immunoglobulin (RhoGAM) to Rh-negative mothers. In cases where HDN has already developed, treatment may include blood transfusions, phototherapy, and exchange transfusion.
Common Queries
What is the most common ATI reproduction complication of pregnancy?
Preeclampsia is the most common ATI reproduction complication of pregnancy, affecting approximately 5-8% of pregnancies worldwide.
What are the signs and symptoms of placental abruption?
Placental abruption can manifest with vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, uterine tenderness, and fetal distress.
How is gestational diabetes diagnosed?
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed through an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) performed between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.