Mixed ionic covalent compounds, a fascinating class of chemical entities, present a unique blend of ionic and covalent bonding characteristics. Embark on a journey into the realm of mixed ionic covalent compound naming, where we unravel the intricate rules that govern the nomenclature of these captivating substances.
Delve into the depths of their nomenclature, exploring the interplay between ionic and covalent bonding, as we decipher the systematic approach to naming these compounds. Discover their captivating properties, comparing them to their ionic and covalent counterparts, and uncover the diverse applications that make them indispensable in various scientific disciplines.
Introduction
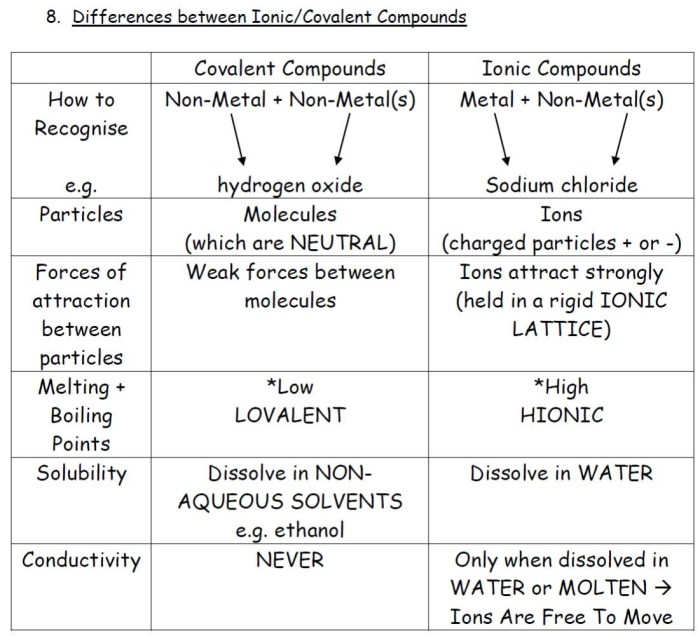
Mixed ionic covalent compounds are compounds that have characteristics of both ionic and covalent compounds. They are formed when a metal reacts with a non-metal, but the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms is not large enough to form a completely ionic compound.
As a result, the bond between the atoms has both ionic and covalent character.
Some examples of mixed ionic covalent compounds include:
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Potassium chloride (KCl)
- Calcium oxide (CaO)
- Magnesium oxide (MgO)
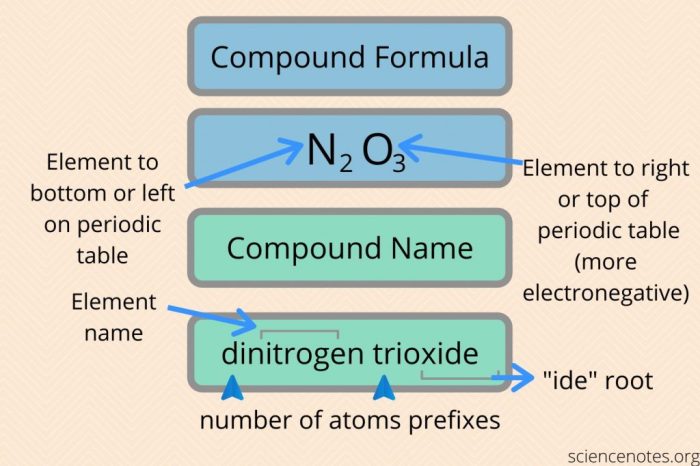
Naming Mixed Ionic Covalent Compounds
The rules for naming mixed ionic covalent compounds are as follows:
- The cation is named first, followed by the anion.
- The cation is named using the same rules as for ionic compounds.
- The anion is named using the same rules as for covalent compounds.
For example, the compound NaCl is named sodium chloride. The cation is Na+, which is named sodium. The anion is Cl-, which is named chloride.
Properties of Mixed Ionic Covalent Compounds
Mixed ionic covalent compounds have properties that are intermediate between those of ionic and covalent compounds.
- They are typically solids at room temperature.
- They have relatively high melting and boiling points.
- They are soluble in water.
- They are good conductors of electricity.
The properties of mixed ionic covalent compounds can be explained by the nature of the bond between the atoms. The ionic character of the bond gives the compound its high melting and boiling points and its solubility in water. The covalent character of the bond gives the compound its ability to conduct electricity.
Applications of Mixed Ionic Covalent Compounds, Mixed ionic covalent compound naming
Mixed ionic covalent compounds are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- As catalysts
- As pigments
- As semiconductors
- As electrolytes
For example, NaCl is used as a catalyst in the production of chlorine gas. KCl is used as a fertilizer. CaO is used as a refractory material. MgO is used as an antacid.
Frequently Asked Questions: Mixed Ionic Covalent Compound Naming
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds involve the complete transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of charged ions. Covalent bonds, on the other hand, arise from the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
How are mixed ionic covalent compounds named?
Mixed ionic covalent compounds are named using a combination of the rules for ionic and covalent compound naming. The metal is named first, followed by the non-metal, with the suffix “-ide” added to the non-metal’s name.
What are some examples of mixed ionic covalent compounds?
Examples of mixed ionic covalent compounds include sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium chloride (KCl), and calcium oxide (CaO).