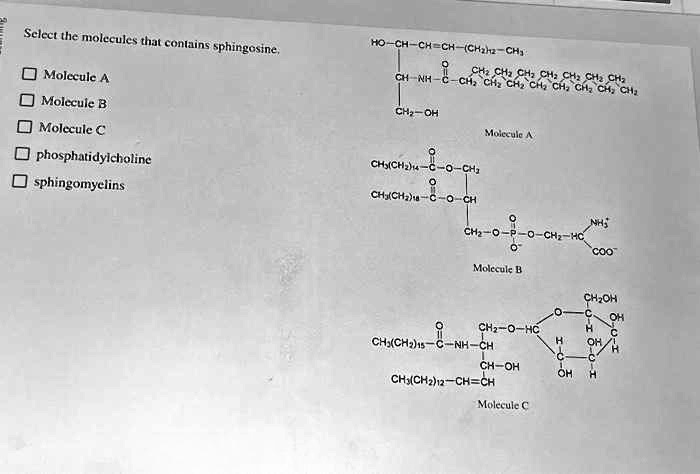
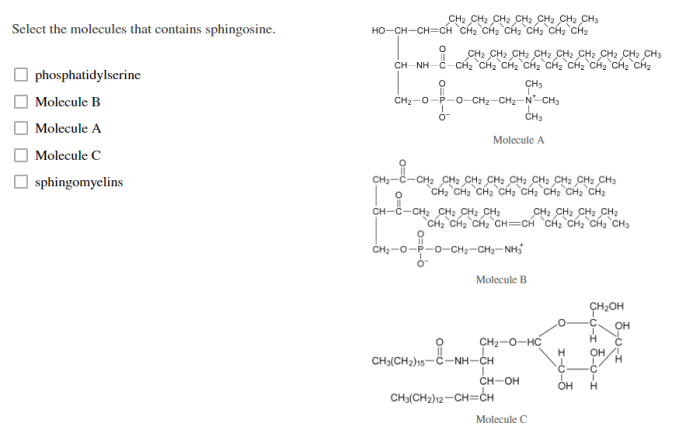
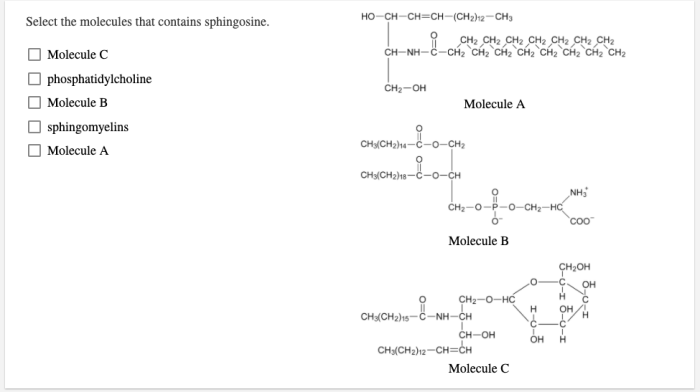
Select the molecules that contains sphingosine – Embark on a scientific journey as we delve into the realm of sphingosine-containing molecules, exploring their structure, functions, and potential therapeutic applications. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the significance of these molecules in biological systems, providing a foundation for further research and advancements in medicine.
Sphingolipids, a class of lipids characterized by the presence of sphingosine, play crucial roles in cellular processes ranging from signal transduction to metabolism. Understanding the molecules that contain sphingosine is essential for unraveling their diverse functions and harnessing their therapeutic potential.
Sphingolipids
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids that contain sphingosine, a long-chain amino alcohol. They are found in the plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells and play important roles in cellular signaling and metabolism.
Structure and Composition
Sphingolipids are composed of three main components: a sphingosine backbone, a fatty acid, and a polar head group. The sphingosine backbone is a long-chain amino alcohol with 18 carbon atoms. The fatty acid is typically a saturated or monounsaturated fatty acid with 16-24 carbon atoms.
The polar head group can be a variety of different molecules, including phosphocholine, phosphoethanolamine, or a carbohydrate.
Role of Sphingosine in Sphingolipid Synthesis
Sphingosine is an essential component of sphingolipids. It is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum from serine and palmitoyl-CoA. The first step in the synthesis of sphingosine is the condensation of serine and palmitoyl-CoA to form 3-ketosphinganine. 3-Ketosphinganine is then reduced to sphinganine, which is finally oxidized to sphingosine.
Molecules Containing Sphingosine
Sphingosine is found in a variety of different molecules, including sphingolipids and non-sphingolipids.
Sphingolipids
- Ceramides
- Sphingomyelins
- Glucocerebrosides
- Galactocerebrosides
- Sulfatides
Non-Sphingolipids
- Sphingosine-1-phosphate
- Sphingosylphosphorylcholine
- Sphingosylceramide
Functions of Sphingosine-Containing Molecules
Sphingosine-containing molecules have a wide range of functions in biological systems.
Sphingolipids
- Structural components of cell membranes
- Regulators of cellular signaling
- Modulators of metabolism
- Effectors of cell death
Sphingosine-1-Phosphate, Select the molecules that contains sphingosine
- Regulator of cell growth and differentiation
- Modulator of vascular tone
- Activator of immune cells
Applications of Sphingosine-Containing Molecules: Select The Molecules That Contains Sphingosine
Sphingosine-containing molecules have a variety of potential therapeutic applications.
Sphingosine-1-Phosphate, Select the molecules that contains sphingosine
- Treatment of multiple sclerosis
- Treatment of cancer
- Treatment of inflammatory diseases
FTY720
- Immunosuppressant
- Treatment of multiple sclerosis
- Treatment of Crohn’s disease
Popular Questions
What is the role of sphingosine in sphingolipid synthesis?
Sphingosine serves as the backbone for sphingolipid synthesis, providing the structural foundation for a diverse array of complex lipids.
How do sphingosine-containing molecules function in biological systems?
Sphingolipids exhibit a wide range of functions, including regulating cellular growth, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune responses.
What are the potential therapeutic applications of sphingosine and its derivatives?
Sphingosine and its derivatives have shown promise in treating various diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions.