Fluid and electrolyte balance heart failure ati – Fluid and electrolyte balance is a critical aspect of maintaining optimal health, particularly in patients with heart failure. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate relationship between fluid and electrolyte homeostasis and heart failure, providing healthcare professionals with a thorough understanding of the pathophysiology, management, and nursing care for patients experiencing fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
The interplay between fluid and electrolyte balance in heart failure is complex and requires careful monitoring and intervention. This guide explores the mechanisms that regulate fluid and electrolyte balance, the consequences of imbalances, and the nursing interventions essential for maintaining electrolyte homeostasis in heart failure patients.
Fluid Balance: Fluid And Electrolyte Balance Heart Failure Ati
Fluids are essential for life, making up approximately 60% of the human body. They play a crucial role in numerous physiological processes, including nutrient transport, waste removal, and temperature regulation.
The body maintains fluid balance through a complex system of mechanisms involving the kidneys, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. The kidneys regulate fluid intake and output, while the lungs and gastrointestinal tract regulate fluid loss through evaporation and excretion.
Consequences of Fluid Imbalances
- Hypovolemia:Fluid deficit, which can lead to hypotension, tachycardia, and electrolyte imbalances.
- Hypervolemia:Fluid overload, which can cause edema, shortness of breath, and heart failure.
Electrolyte Balance
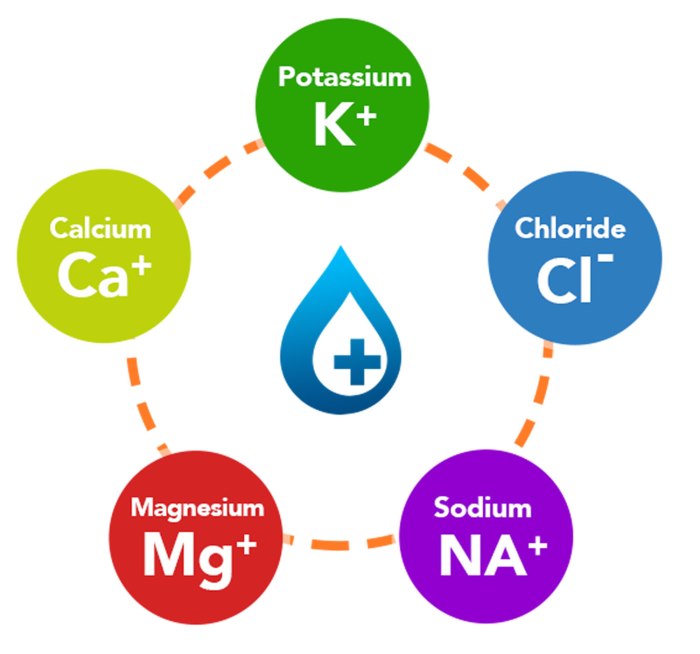
Electrolytes are minerals that carry an electrical charge when dissolved in water. They play essential roles in maintaining osmotic pressure, regulating muscle function, and transmitting nerve impulses.
The body regulates electrolyte balance through the kidneys, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. The kidneys regulate electrolyte intake and output, while the lungs and gastrointestinal tract regulate electrolyte loss through evaporation and excretion.
Consequences of Electrolyte Imbalances, Fluid and electrolyte balance heart failure ati
- Hyponatremia:Low sodium levels, which can cause seizures, coma, and even death.
- Hypernatremia:High sodium levels, which can cause dehydration, muscle weakness, and confusion.
- Hypokalemia:Low potassium levels, which can cause muscle weakness, arrhythmias, and paralysis.
- Hyperkalemia:High potassium levels, which can cause muscle weakness, arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest.
Fluid and Electrolyte Balance in Heart Failure
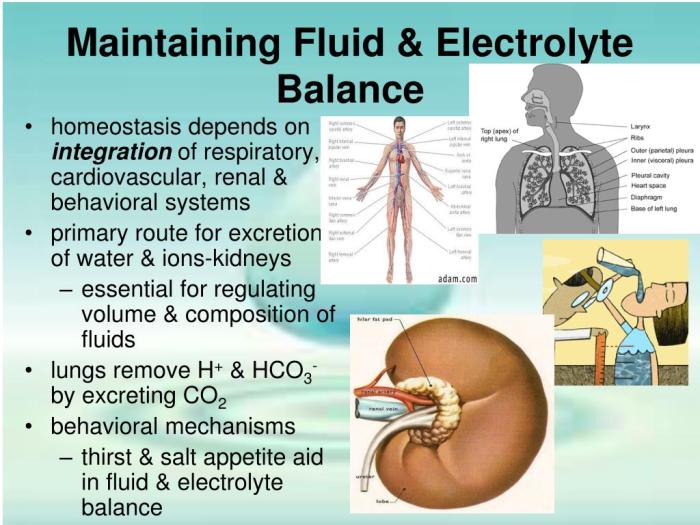
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This can lead to fluid and electrolyte imbalances due to impaired renal function and increased capillary permeability.
Fluid overload is a common complication of heart failure, leading to edema, shortness of breath, and pulmonary congestion. Electrolyte imbalances, particularly hyponatremia and hyperkalemia, are also common and can contribute to the symptoms and progression of heart failure.
Management of Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances in Heart Failure
- Diuretics:Used to reduce fluid overload and improve renal function.
- Sodium restriction:May be recommended to prevent hyponatremia.
- Potassium supplements:May be necessary to correct hypokalemia.
- Dialysis:May be required in severe cases of fluid overload or electrolyte imbalance.
Nursing Care for Patients with Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances
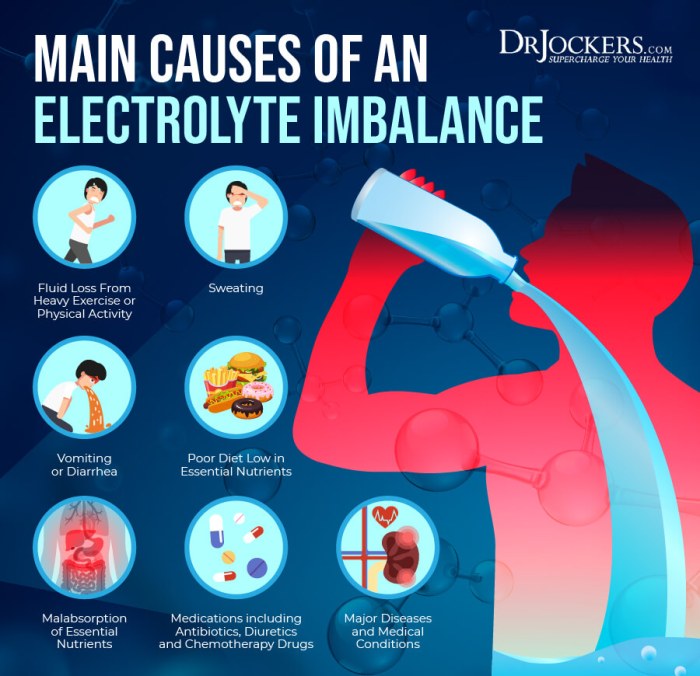
Nurses play a vital role in assessing, managing, and educating patients with fluid and electrolyte imbalances. They must be able to:
- Identify the signs and symptoms of fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
- Monitor fluid intake and output.
- Administer medications as prescribed.
- Provide patient education on fluid and electrolyte balance.
Importance of Patient Education
Patient education is crucial for the prevention and management of fluid and electrolyte imbalances. Nurses must educate patients on the following:
- Importance of maintaining adequate fluid intake.
- Symptoms of fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
- Dietary modifications to prevent or manage imbalances.
- Importance of medication adherence.
FAQ Corner
What are the common signs and symptoms of fluid overload in heart failure?
Common signs and symptoms of fluid overload in heart failure include shortness of breath, swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet, rapid weight gain, fatigue, and decreased urine output.
What are the potential consequences of electrolyte imbalances in heart failure?
Electrolyte imbalances in heart failure can lead to a range of complications, including arrhythmias, muscle weakness, seizures, and even death.
How is fluid and electrolyte balance managed in patients with heart failure?
Management of fluid and electrolyte balance in heart failure typically involves a combination of diuretics, sodium restriction, and potassium supplements. In severe cases, intravenous fluids and electrolyte replacement therapy may be necessary.