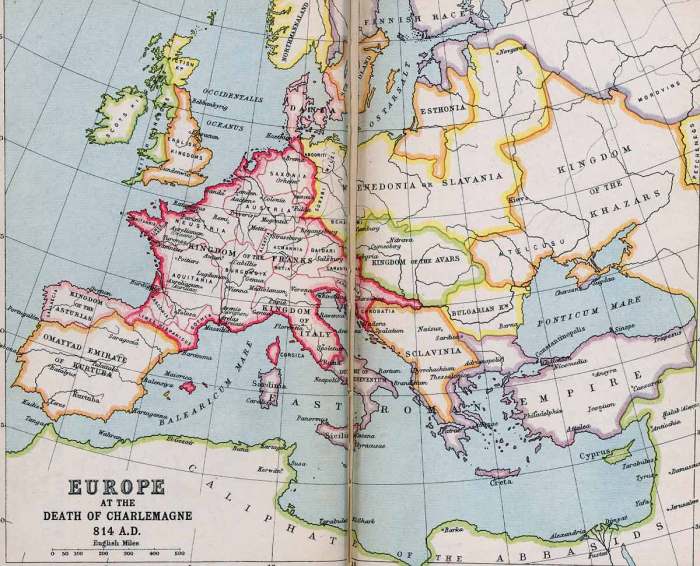
Map of europe in charlemagne’s time – Embarking on an exploration of Europe during Charlemagne’s reign, this comprehensive guide delves into the extent, borders, and major cities of his vast empire. A detailed map serves as a visual aid, guiding us through Charlemagne’s military conquests, administrative structure, and cultural legacy.
From the Carolingian Renaissance to the impact on European history, Charlemagne’s reign shaped the political, cultural, and religious landscape of the continent. This guide unravels the complexities of his empire, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance.
Charlemagne’s Empire
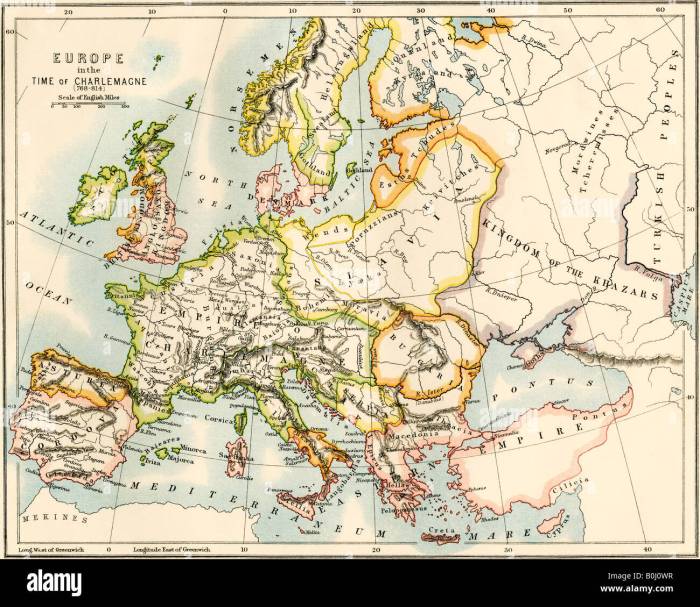
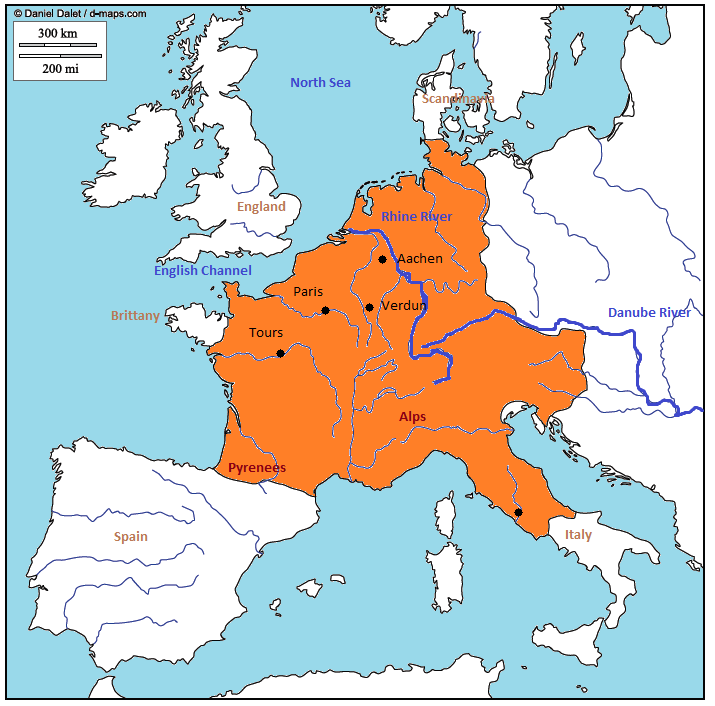
Charlemagne’s empire, also known as the Carolingian Empire, was one of the largest and most powerful empires in European history. It stretched from the Pyrenees Mountains in the west to the Elbe River in the east, and from the North Sea in the north to the Mediterranean Sea in the south.
The empire was divided into several kingdoms, each ruled by a member of Charlemagne’s family.
Charlemagne’s empire was a major center of learning and culture. He founded the Palace School at Aachen, which became one of the most important centers of learning in Europe. He also encouraged the development of art and architecture, and many of the most famous buildings in Europe were built during his reign.
Major Cities and Regions
The major cities of Charlemagne’s empire included:
- Aachen: The capital of the empire and the site of Charlemagne’s palace.
- Paris: The capital of the Frankish kingdom.
- Rome: The capital of the Papal States.
- Ravenna: The capital of the Exarchate of Ravenna.
- Constantinople: The capital of the Byzantine Empire.
The major regions of Charlemagne’s empire included:
- Francia: The core of the empire, which included the Frankish kingdom and the Duchy of Aquitaine.
- Lombardy: The kingdom of the Lombards in northern Italy.
- Saxony: The kingdom of the Saxons in northern Germany.
- Bavaria: The kingdom of the Bavarians in southern Germany.
- Pannonia: The kingdom of the Avars in central Europe.
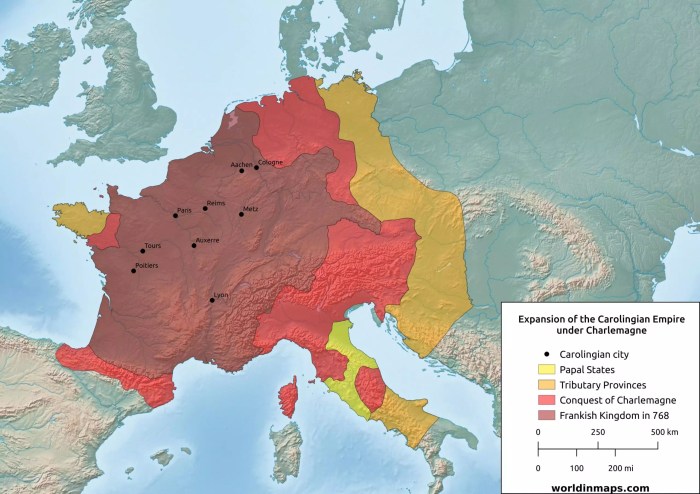
Charlemagne’s Conquests
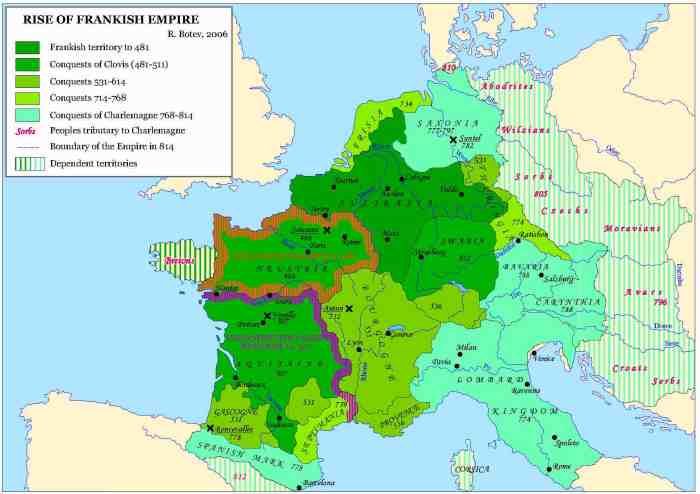
Charlemagne’s reign marked a period of significant territorial expansion and military conquest. Through a series of strategic campaigns, he extended the Frankish kingdom to encompass a vast empire that stretched across much of Western and Central Europe.
Charlemagne’s Strategies and Tactics
Charlemagne’s armies employed a combination of strategies and tactics that contributed to their success on the battlefield. These included:
-
-*Mobility
Charlemagne’s armies were highly mobile, utilizing cavalry to rapidly move across vast distances and strike at enemy strongholds.
-*Siege warfare
Charlemagne’s armies were skilled in siege warfare, using siege engines and other techniques to capture fortified cities and castles.
-*Infantry formations
Charlemagne’s infantry fought in disciplined formations, such as the shield wall, which provided a formidable defensive barrier against enemy attacks.
-*Logistics and organization
Charlemagne ensured that his armies were well-supplied and organized, with efficient supply lines and a system of communication that allowed for coordinated maneuvers.
Timeline of Charlemagne’s Major Battles and Victories
-
-*772
Conquest of the Lombards in Italy
-*773-774
Saxon Wars in Germany
-*778
Battle of Roncevaux Pass (Basque uprising)
-*785
Conquest of Bavaria
-*791
Avar Wars in Central Europe
-*796-801
Conquest of the Saxons in Northern Germany
-*800
Coronation as Holy Roman Emperor
-*806
Conquest of Bohemia
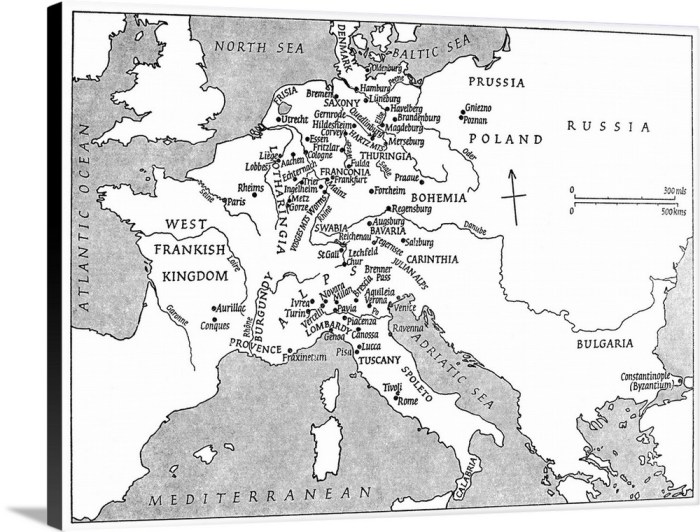
Charlemagne’s Administration
Charlemagne’s vast empire required an efficient administrative structure to maintain order and stability. The emperor implemented a system that combined elements from Roman, Frankish, and Christian traditions.
The empire was divided into provinces, each governed by a count. Counts were responsible for collecting taxes, administering justice, and leading local military forces. In border regions or areas with a strong local nobility, Charlemagne appointed dukes, who had greater authority and commanded larger armies.
Legal System and Laws
Charlemagne standardized the legal system across his empire, drawing inspiration from Roman law and Christian principles. He issued a series of laws known as capitularies, which covered a wide range of topics, including criminal justice, property rights, and ecclesiastical matters.
The laws emphasized the importance of maintaining peace and order, protecting the weak, and promoting justice. They also reflected Charlemagne’s desire to create a unified Christian empire, incorporating religious principles into the legal framework.
Charlemagne’s Cultural Legacy
Charlemagne’s reign marked a period of significant cultural revival known as the Carolingian Renaissance. This revival was characterized by a renewed interest in classical learning, art, and architecture, which laid the foundation for the development of European culture in the Middle Ages.
Role of Monasteries and Scholars
Monasteries played a pivotal role in preserving and transmitting knowledge during Charlemagne’s reign. They served as centers of learning, housing libraries and providing education to monks and scholars. Notable scholars of this period included Alcuin of York, who established the palace school at Aachen, and Einhard, Charlemagne’s biographer.
Key Cultural Achievements
| Achievement | Significance |
|---|---|
| Carolingian Minuscule | A standardized script that improved legibility and facilitated the dissemination of written works. |
| Carolingian Architecture | A blend of Romanesque and Byzantine styles, exemplified by the Palatine Chapel in Aachen. |
| Carolingian Art | Characterized by intricate metalwork, illuminated manuscripts, and ivory carvings. |
| Revival of Latin Learning | Translation and preservation of classical texts, fostering a renewed interest in Roman literature and philosophy. |
Charlemagne’s Impact on Europe
Charlemagne’s empire had a profound and lasting impact on the course of European history. It marked a significant turning point in the development of Europe, shaping its political, cultural, and religious landscape for centuries to come.
Political Legacy
Charlemagne’s empire was a major force in stabilizing and unifying Western Europe after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. It established a centralized authority that provided security and stability, fostering economic growth and cultural exchange.
- Creation of a Centralized State:Charlemagne’s empire brought together a vast and diverse territory under a single ruler, creating a unified political entity that had not existed in Europe for centuries.
- Strengthening of Royal Power:Charlemagne’s coronation as emperor by Pope Leo III in 800 AD significantly enhanced the authority of the monarchy, establishing the concept of a Christian emperor ruling over a unified Europe.
- Feudal System:Charlemagne’s empire implemented a feudal system, where land was granted to nobles in exchange for military service. This system became a cornerstone of European society for centuries, shaping political and social relations.
Cultural Legacy, Map of europe in charlemagne’s time
Charlemagne’s reign witnessed a significant revival of learning and culture, known as the Carolingian Renaissance. He actively promoted education, establishing schools and libraries throughout his empire.
- Preservation of Classical Knowledge:Charlemagne’s scholars preserved and disseminated classical Greek and Roman texts, ensuring their survival and influence on later European thought.
- Carolingian Architecture:The Carolingian period saw the development of a distinctive architectural style characterized by round arches, thick walls, and ornate decorations, which became influential in subsequent European architecture.
- Liturgical Reforms:Charlemagne introduced standardized liturgical practices throughout his empire, unifying religious rituals and fostering a sense of Christian community.
Religious Legacy
Charlemagne’s empire played a pivotal role in the spread of Christianity throughout Europe. He supported missionary activities and established close ties with the Catholic Church.
- Christianization of Northern Europe:Charlemagne’s conquests and missionary efforts brought Christianity to large parts of Northern Europe, including Germany, Scandinavia, and Eastern Europe.
- Papal Supremacy:Charlemagne’s coronation by the Pope strengthened the authority of the papacy and established a close relationship between the Frankish monarchy and the Catholic Church.
- Establishment of Monasteries:Charlemagne encouraged the establishment of monasteries throughout his empire, which became centers of learning, religious life, and economic activity.
Comparative Analysis
Charlemagne’s empire ranks among the most significant empires in European history. It can be compared to other major empires in terms of its size, influence, and legacy.
| Empire | Period | Size | Influence | Legacy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roman Empire | 27 BC
|
Vast territory spanning Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East | Established a unified Mediterranean world, spreading Roman law, culture, and infrastructure | Foundation of Western civilization, lasting impact on law, government, and architecture |
| Byzantine Empire | 330
|
Eastern Roman Empire centered on Constantinople | Preserved Greek and Roman culture, developed Eastern Orthodox Christianity | Influenced Slavic and Eastern European civilizations, architectural marvels such as Hagia Sophia |
| Carolingian Empire | 768
|
Western Europe, including France, Germany, and Italy | Unified Europe after the fall of the Western Roman Empire, revived learning and culture | Shaped European political, cultural, and religious landscape for centuries, laid the foundation for modern Europe |
Frequently Asked Questions: Map Of Europe In Charlemagne’s Time
What was the extent of Charlemagne’s empire?
Charlemagne’s empire encompassed much of Western and Central Europe, including present-day France, Germany, Italy, and parts of Spain and Eastern Europe.
What were the major cities of Charlemagne’s empire?
Major cities included Aachen (the imperial capital), Rome, Paris, and Constantinople.
What was the impact of Charlemagne’s reign on European culture?
Charlemagne’s reign ushered in the Carolingian Renaissance, a period of cultural and intellectual revival that preserved and transmitted classical knowledge.